Work and Energy
Q1. A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force. Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement. What is the work done in this case?
Answer : F=7N ,s = 8 m
W = F × s
= 7 N × 8 m
W = 56J
∴ Work done is 56 J.
Q2. When do we say that work is done?
Answer : Work is said to be done when a force causes displacement of an object in
the direction of applied force.
Q3. Write an expression for the work done when a force is acting on an object in
the direction of its displacement.
Answer :Work done = Force x Displacement
Q4. Define 1J of work.
Answer : 1 Joule of work is said to be done when a force of 1N causes a displacement
of 1m in its own direction .
Q5. A pair of bullocks exerts a force of 140 N on a plough. The field being
ploughed is 15 m long. How much work is done in ploughing the length of the
field?
Answer : Force = 140 N
s = 15m
W = ?
W = F × s
= 140 N x 15 m
= 2100 Nm
W = 2100 J
∴ Work done in ploughing the length of the field is 2100 J.
Q6. What is the kinetic energy of an object?
Answer : The energy possessed by an object by virtue of its motion is called
kinetic energy of an object.
Q7. Write an expression for the kinetic energy of an object.
Answer : If a body of mass m is moving with a velocity v, then its kinetic energy K.E is
given by the expression, K.E = 1/2 mv2.
Q8. The kinetic energy of an object of mass, m moving with a velocity of 5 m/s is 25 J.
What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is doubled? What will be its kinetic
energy when its velocity is increased three times.
Answer : Using the formula for the kinetic energy we have : 
or 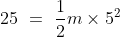
or 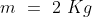
i) Kinetic energy when velocity is doubled : V= 2 x 5 = 10

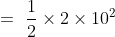
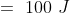
(ii) Kinetic energy when velocity is tripled : 3 x 5 =15

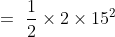
or 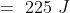
Q9. What is power ?
Answer : Power is defined as the rate of doing work.
Q10. Define 1 watt of power.
Answer : Power is said to be 1 watt when 1 Joule work is done in 1 second.
Q11. A lamp consumes 1000 J of electrical energy in 10 s. What is its power?
Answer : Given W = 1000J, t = 10s, P =?
We know, P = W/t = 1000/10 = 100W
Q12. Define average power.
Answer : Average power is defined as the total energy consumed divided by the
total time taken.
Q13. Look at the activities listed below. Reason out whether or not work is done in
the light of your understanding of the term ‘work’.
(a) Suma is swimming in a pond.
Answer : Yes. Suma is doing work. She pushes water in the backward direction and the
displacement is in forward direction.
(b) A donkey is carrying a load on its back.
Answer : No,While carrying a load, the donkey has to apply a force in the upward
direction.But, displacement of the load is in the forward direction. Since, displacement
is perpendicular to force, the work done is zero.
c) A wind mill is lifting water from a well.
Answer : yes, when a windmill is lifting a water from well, it is applying a force in
the upward direction, and it is moving water in the upward direction. Since
displacement and force are in the same direction , work is done.
(d) A green plant is carrying out photosynthesis.
Answer : In this case, there is no force involved when a green plant is carrying
photosynthesis and no displacement takes place . Therefore work done is Zero.
(e) An engine is pulling a train.
Answer : An engine applies force to pull the train. This allows the train to move in
the direction of force. Therefore, there is a displacement in the train in the same direction.
Hence, work is done by the engine on the train.
(f) Food grains are getting dried in the sun.
Answer : When food grains are getting dried in the Sun, there is no force
involved. Hence, the work done is zero during the process of food grains
getting dried in the Sun.
(g) A sailboat is moving due to wind energy.
Answer: When a sailboat is moving due to wind energy, force is applied by
the boat in the forward direction. Therefore, there is a displacement in the
boat in the direction of force. Hence, work is done by wind on the boat.
14. An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and
falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie
on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the
object?
Answer : Since the body returns to a point which is on the same horizontal line through
the point of projection, no displacement has taken place against the force of gravity,
therefore, no work is done by the force due to gravity.
15. A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Answer: A battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy
is converted into light energy as the bulb is lighted up, i.e., the sequence of energy
changes is as follows : Chemical energy → Electrical energy → Light energy.
16. A mass of 10 kg is at a point A on a table. It is moved to a point B. If the line
joining A and B is horizontal, what is the work done on the object by the
gravitational force? Explain your answer.
Answer : The work done is zero. This is because the gravitational force and displacement
are perpendicular to each other.
17. The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively.
Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
Answer : It does not violate the law Of conservation of energy. Whatever, is the decrease in PE due to loss of height, same is the increase in the KE due to increase in velocity
of the body.
18. What are the various energy transformations that occur when you
are riding a bicycle?
Answer : While riding a bicycle,the muscular energy of the rider gets transferred to
heat energy and kinetic energy of the bicycle.
19. Does the transfer of energy take place when you push a huge rock with
all your might and fail to move it? Where is the energy you spend going?
Answer :. No, the transfer of energy will not take place when we push a huge rock
and fail to move it.
No loss of energy will take place because the applied muscular energy will be
converted into heat energy which will heat up the body.
20. A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month.
How much energy is this in joules?
Answer : Energy consumed by certain households in a month
E=250 units =250 k Wh
∴E=250×3.6×106 J (∵1kWh=3.6×106J)
⟹E=9×108 Joules
21. An object of mass 40 kg is raised to a height of 5 m above the ground.
What is its potential energy?
If the object is allowed to fall, find its kinetic energy when it is half-way down.Answer :
Given :Mass of the object M=40kgHeight upto which it is raised h=5 m
Potential energy P.E=Mgh
P.E=40×10×5=2000J
Let its kinetic energy be Ek when it is half way down i.e h′=h2
According to conservation of energy,
K.Ei+P.Ei=K.Ef+P.Ef
0+2000=Ek+Mgh2
∴ 2000=Ek+40×10×52
⟹Ek=1000
Work is done because the displacement of water takes place and a force is applied by the wind mill. Wind mill does a work against gravity.Work is done because the displacement of water tak2es place and a force is applied by the wind mill. Wind mill does a work against gravity.

No comments:
Post a Comment